Automation
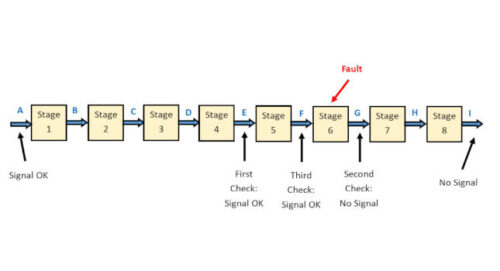
Automation uses devices, system, components and networks, often independent of human interaction, to operate safely in manufacturing by increasing efficiency, improving quality, and reducing costs. Automation can be used in a variety of manufacturing processes, including material handling, assembly, inspection, testing and packaging.
Automation Articles
Automation helps combat labor shortages
Think Again: Are automation and controls helping to fill the growing manufacturing skills gap? Control Engineering research, “Purchasing Considerations for Automation Systems & Control Systems” shows an increase in spending for the next 12 months in most categories.
Research suggests many are filling the growing manufacturing skills gap with automation and controls. Control Engineering research, “Purchasing Considerations for Automation Systems & Control Systems” shows an increase in spending for the next 12 months in most categories. Survey respondents were given a list of 15 product categories in automation processes; of those, respondents expected to increase in spending in 14 categories in the next 12 months. Among a list of 39 control system categories, respondents expect spending increases for all 39 in the next 12 months.
Click here to download the survey.
Other ways to fill the skills gap include salary, benefits, training, retention and workforce amenities. These are among the suggestions from the Control Engineering Career and Salary Survey, 2022, other Control Engineering research, related articles on the following pages and news on the prior pages. Find more advice in a May 25 webcast, “Automation experts wanted: Hire, retain the best.”
Survey methods for purchasing study
The purchasing study was conducted by Control Engineering to obtain insights from automation engineering professionals on purchasing automation systems and control systems across process, discrete and hybrid industries. Study sample was selected from qualified subscribers of Control Engineering media with valid email addresses and involved in the purchase or specification of control systems, including human-machine interfaces (HMIs), programmable logic controllers (PLCs), programmable automation controllers (PACs), distributed control systems (DCSs), single-loop controllers or PC-based controllers. The email included a URL linked to the questionnaire and data collected March 3 through March 11, 2022. With 158 respondents, the margin of error was +/-7.8% at a 95% confidence level.
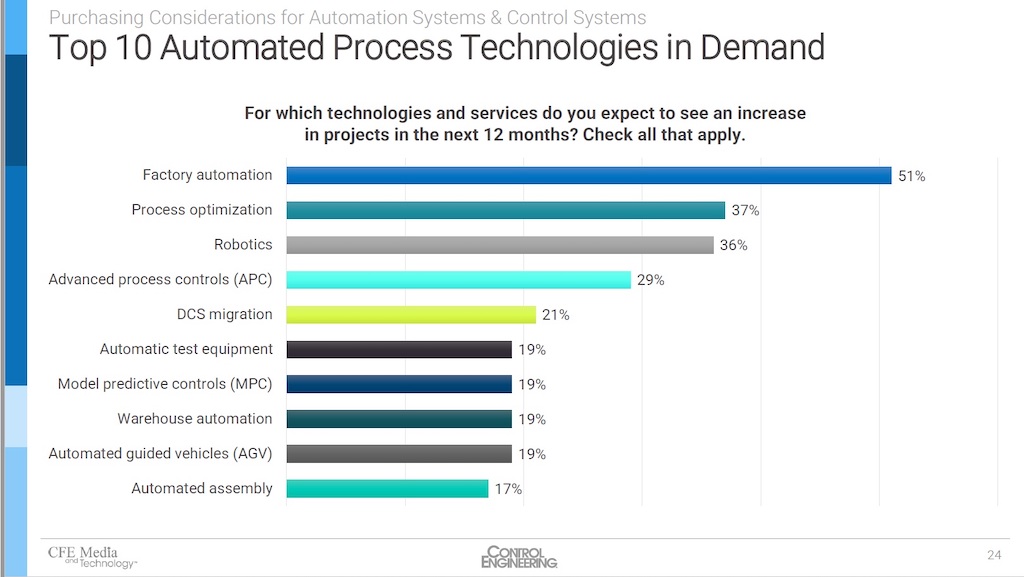 Factory automation, process optimization and robotics were the leading three automated technologies and services survey respondents expect to see in the next 12 months.
Factory automation, process optimization and robotics were the leading three automated technologies and services survey respondents expect to see in the next 12 months.
Courtesy: Control Engineering 2022 research, “Purchasing Considerations for Automation Systems & Control Systems”
New automation, replacements, upgrades, system integration
Among respondents, average automation system, control system budget breakdown spreads around investments with 28% for new automation systems and/or control systems,
25% for replacement equipment for automation systems and/or control systems, 22% upgrading automation systems and/or control systems and 18% for system integration and services (including programming) related to automation systems and/or control systems and 7% to other areas.
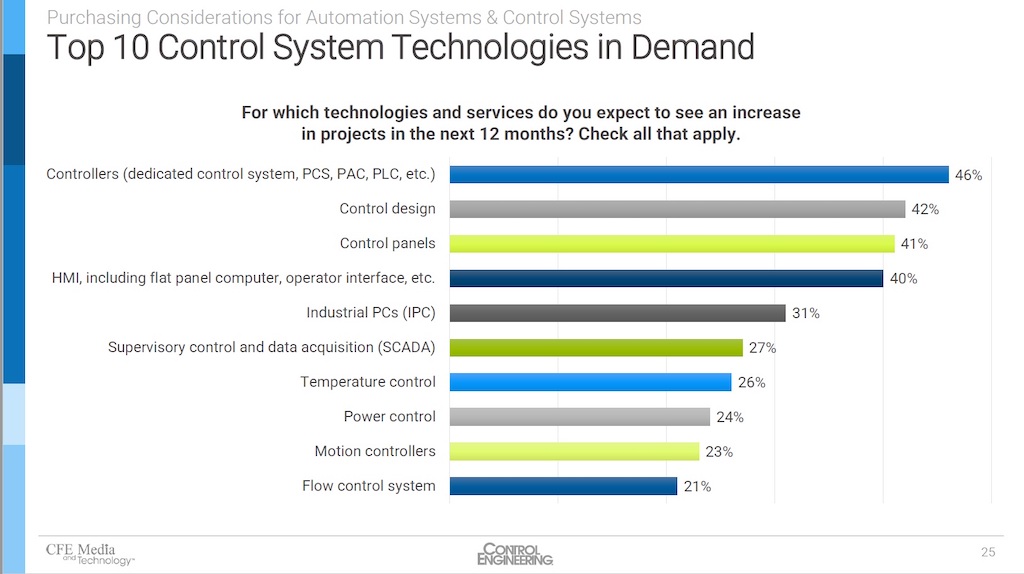 Controllers (dedicated control system, PCS, PAC, PLC, etc.), control design, control panels; and human-machine interface (HMI), including flat panel computer, operator interface, etc., are the leading control system technologies increasing in the next 12 months. Courtesy: Control Engineering 2022 research, “Purchasing Considerations for Automation Systems & Control Systems”
Controllers (dedicated control system, PCS, PAC, PLC, etc.), control design, control panels; and human-machine interface (HMI), including flat panel computer, operator interface, etc., are the leading control system technologies increasing in the next 12 months. Courtesy: Control Engineering 2022 research, “Purchasing Considerations for Automation Systems & Control Systems”
Top 10 automated process technologies in demand
Respondents were asked for which automated technologies and services do you expect to see an increase in projects in the next 12 months? The top 10 are:
- 51% Factory automation
- 37% Process optimization
- 36% Robotics
- 29% Advanced process controls (APC)
- 21% DCS migration
- 19% Automatic test equipment
- 19% Model predictive controls (MPC)
- 19% Warehouse automation
- 19% Automated guided vehicles (AGV)
- 17% Automated assembly.
Top 10 control system technologies in demand
The top 10 control system technologies increasing in the next 12 months are:
- 46% Controllers (dedicated control system, PCS, PAC, PLC, etc.)
- 42% Control design
- 41% Control panels
- 40% HMI, including flat panel computer, operator interface, etc.
- 31% Industrial PCs (IPC)
- 27% Supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA)
- 26% Temperature control
- 24% Power control
- 23% Motion controllers
- 21% Flow control system.
Automation and controls help improve throughput, improve quality, lower costs, reduce waste, and make companies more competitive in their markets. Automation and controls also help fewer available workers do their jobs better.
Other areas covered in the purchasing study include:
- Top 10 ways a vendor can win new business
- Implementing and maintaining systems
- Time spent researching and purchasing systems
- Length of research and evaluation process for new products
- Recent changes to research and evaluation process
- Committee involvement for purchases
- Sourcing automation systems, control systems
- Top 10 ways a vendor can retain customers
- Willingness to consider other purchasing options
- Automation system and control system technologies in demand.
Getting ahead with automation, helping to fill the skills gap
Think again about how investments in automation and controls can help optimize, fill the skills gap, and improve offerings for customers.
Mark T. Hoske is content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media and Technology at mhoske@cfemedia.com. Amanda Pelliccione, director of research and awards programs for CFE Media and Technology, conducted the research and assembled the related report.
CONSIDER THIS
How are you expanding automation and controls?
Automation FAQ
-
What are the three basic steps of automation?
The three basic steps of automation are defined in the control loop:
- Sensing: The process of collecting data from the system being automated, typically using sensors or other data collection devices.
- Processing: The process of analyzing the data collected from the system, making decisions based on that data and executing actions based on those decisions.
- Actuation: The process of implementing the decisions made during the processing step, typically by controlling physical devices, such as motors, valves or actuators.
These steps are often repeated continuously, allowing the automation system to continuously monitor and control the system being automated. The specific steps involved in an automation project will depend on the specific requirements of the system being automated and the type of automation being used.
-
What are the biggest challenges in automation?
- Integration: Integrating the various components of an automation system, including sensors, controllers and actuators along with communications among them, can be challenging and require a thorough understanding of the system being automated.
- Cost: Automation can be expensive, depeding on the application, requiring a significant investment in hardware, software and infrastructure.
- Complexity: Automation systems can be complex, requiring specialized knowledge and skills to design, implement and maintain, especially with systems of higher variability.
- Cybersecurity: Automation systems can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks, requiring robust cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Maintenance: Automation systems may require monitoring and regular maintenance to ensure that they continue to operate as intended, which may be time-consuming and resource-intensive.
- Scalability: Automation systems need to be scalable to accommodate growth and changing requirements, which can be challenging and require careful planning.
- Human factors: Automation can have an impact on human workers, requiring a careful approach to ensure that they are supported and trained to work effectively with automated systems.
-
How will automation change manufacturing?
- Increased efficiency: Automation is expected to increase the efficiency of manufacturing processes by reducing variability and ensuring that processes operate within desired limits.
- Improved quality: Automation is expected to improve the quality of manufactured products by reducing variability and ensuring that processes operate within desired limits.
- Enhanced safety: Automation is expected to improve the safety of manufacturing processes by reducing the need for manual handling of hazardous materials and reducing the risk of human error.
- Reduced labor costs: Automation is expected to reduce the need for manual labor in manufacturing, reducing labor costs and allowing manufacturers to be more competitive in the global marketplace.
- Improved speed and responsiveness: Automation is expected to improve the speed and responsiveness of manufacturing processes, allowing manufacturers to meet customer demands more quickly and effectively.
- Increased flexibility: Automation is expected to increase the flexibility of manufacturing processes, allowing manufacturers to quickly adapt to changing market conditions and customer demands.
-
Why does automation in manufacturing matter?
Automation in manufacturing can bring improved efficiency, quality, competitiveness, safety, scalability, and sustainability to organizations. Automated systems reduce manual labor, increase production speed and accuracy, improve safety, and enable quick scaling to meet changing demand. This results in reduced costs, improved productivity, and a more environmentally friendly production process.
Some FAQ content was compiled with the assistance of ChatGPT. Due to the limitations of AI tools, all content was edited and reviewed by our content team.